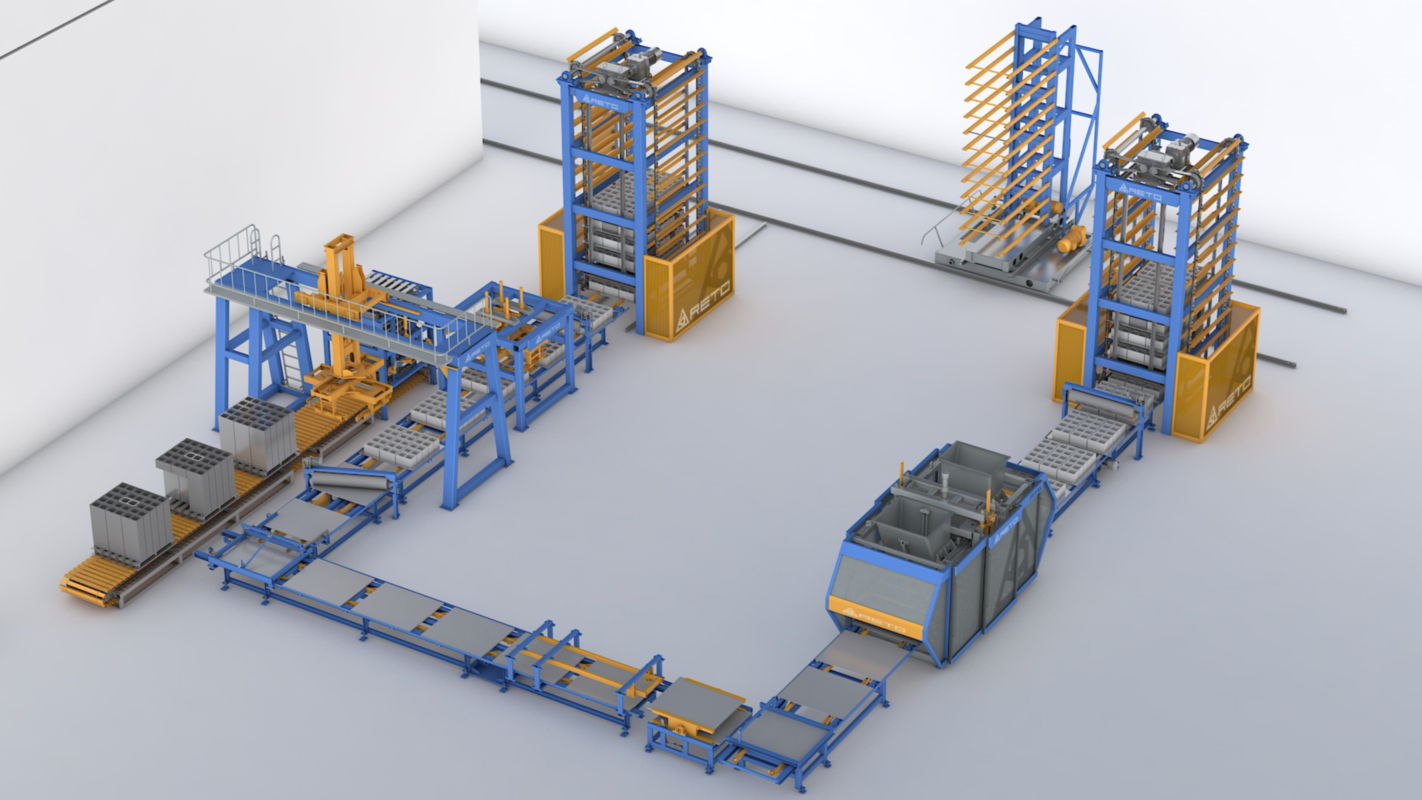
Quality control measures in cement block machines are critical to ensuring the consistency, strength, and durability of produced blocks.
Some of the key quality control measures integrated into these machines include:
- Material Proportioning and Mixing Control: Precise control over the proportioning of aggregates, cement, water, and additives ensures the correct mix consistency. Some machines incorporate automated systems to precisely measure and mix materials to the required ratios, reducing human error.
- Vibration and Compaction Control: Block machines use vibration and compaction mechanisms to consolidate the material mix within the molds. Control systems regulate the intensity and duration of vibrations to ensure uniform compaction and density across all blocks.
- Mold Design and Precision: Block machines have molds designed to produce blocks of specific dimensions and shapes. Quality control measures ensure the accuracy and precision of these molds, ensuring uniformity and consistency in block size and shape.
- Automated Block Ejection and Handling: Controlled ejection of formed blocks from molds minimizes damage and maintains the integrity of the blocks. Automated handling systems prevent block breakage or deformities during removal from the molds.
- Real-Time Monitoring and Sensors: Some machines incorporate sensors to monitor various parameters during production, such as material flow, pressure, temperature, and block dimensions. Real-time data helps detect deviations and allows for immediate corrective actions.
- Quality Inspection and Rejection Systems: Automated or manual inspection stations check blocks for defects, irregularities, or inadequate compaction. Defective blocks are rejected, ensuring only high-quality blocks move to the curing or stacking phases.
- Curing Control: Block machines may have systems to control the curing process, ensuring consistent curing conditions such as temperature and humidity to optimize block strength and durability.
- Operator Training and Guidelines: Training programs and guidelines ensure machine operators understand quality standards, machine operation, and maintenance protocols. Skilled operators can better maintain quality throughout the production process.
- Quality Assurance Certifications: Some manufacturers may adhere to industry-specific quality assurance standards or certifications to guarantee the quality of produced blocks.
By integrating these quality control measures into cement block machines, manufacturers can ensure that the blocks produced meet specified standards, resulting in durable, high-quality construction materials for various applications.
How does cement block machine cater to custom block designs and shapes?
Cement block machines can cater to custom block designs and shapes through several mechanisms:
- Interchangeable Molds: Many modern block machines are designed with interchangeable molds. These molds can be easily swapped out to produce blocks of different shapes, sizes, and surface textures, allowing for customization.
- Custom Mold Fabrication: Manufacturers or users can request custom molds to produce specific block designs. These molds are created based on the desired design specifications, enabling the production of unique blocks.
- Adjustable Compression and Vibration: Block machines allow adjustments in compression force and vibration intensity. cement block machine This flexibility helps in achieving different block densities, shapes, and surface finishes according to custom requirements.
- Specialized Attachments: Some machines have specialized attachments or additional components that can be added to the machine to create specific block designs or features.
- Software Control: Advanced machines might have software controls that allow for programming and customization of block designs. These systems enable operators to input design specifications, controlling the machine to produce custom blocks accordingly.
- Manual Adaptation: In some cases, operators can manually adapt the machine’s settings or configurations to produce custom blocks, especially if the machine allows for manual adjustments.
- Prototype Testing: Block machines can be used to produce prototypes of custom block designs. Once the prototype is tested and approved, the machine can then be adjusted to produce these blocks in larger quantities.
- Collaboration with Manufacturers: Manufacturers of block machines often collaborate with clients to understand their specific design requirements. They may offer expertise and solutions tailored to achieve the desired custom block shapes and designs.
The adaptability of block machines to cater to custom block designs and shapes depends on the machine’s design, capabilities, and the level of customization required. With the right adjustments, settings, and mold configurations, these machines can produce a wide variety of block designs to meet specific project needs.